Function, Design, and Technological Advancements”
The crankshaft, or “Kurbelwelle” in German, is a fundamental issue in internal combustion engines, chargeable for converting the linear motion of pistons into rotational motion that in the long run powers a vehicle’s drivetrain. This difficult piece of engineering has gone through big improvements through the years, enhancing engine performance, efficiency, and durability.
Design and Functionality
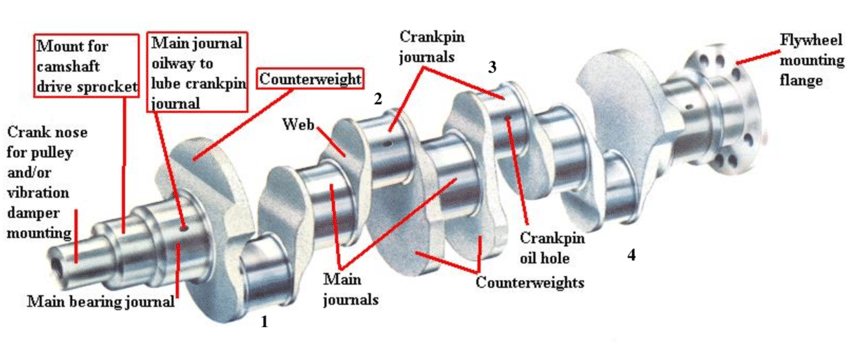
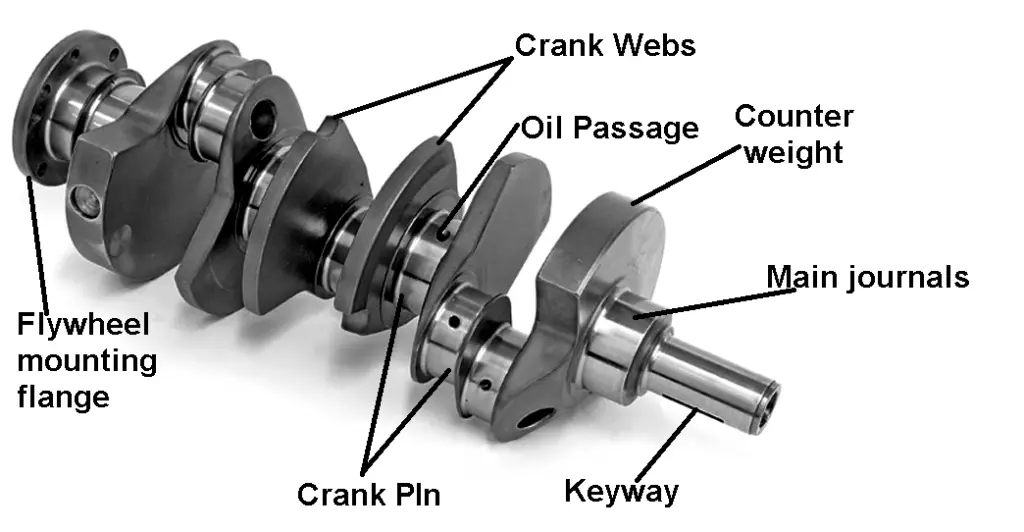
At its middle, the crankshaft transforms the up-and-down motion of pistons into rotational motion. Each piston connects to the crankshaft thru a connecting rod, with the crankshaft’s offset crankpins (additionally referred to as rod bearing journals) facilitating this conversion. The precise association and balancing of those additives are vital for smooth engine operation.
In V8 engines, number one crankshaft configurations are typical: move-plane and flat-aircraft. Cross-aircraft crankshafts have crank throws spaced ninety levels aside, contributing to smoother operation and reduced vibration. In evaluation, flat-aircraft crankshafts function throws spaced a hundred and eighty degrees aside, bearing in mind higher engine speeds but frequently ensuing in increased vibration. The desire between these configurations substantially affects engine characteristics, influencing factors which includes stability, overall performance, and sound.
Manufacturing Techniques
The manufacturing of crankshafts has advanced to incorporate numerous techniques, every providing wonderful blessings:
- Forging: This procedure includes shaping the crankshaft from a metallic bar the use of compressive forces. Forged crankshafts are famend for his or her energy and sturdiness, making them appropriate for excessive-overall performance applications. The use of vanadium micro-alloyed steels in forging allows for air-cooling after achieving high strengths without extra warmness treatment, improving performance and lowering charges.
- Casting: In this method, molten metallic is poured right into a mildew to shape the crankshaft. Cast crankshafts, generally made from ductile iron, are extra fee-effective and are usually discovered in popular manufacturing engines where the demands are much less strenuous.
- Machining from Billet: This method entails carving the crankshaft from a strong piece of tremendous metal. While supplying amazing precision and the capability to apply superior materials, it’s far a time-consuming and pricey procedure, frequently reserved for custom or high-overall performance engines.
Advancements in production technology, which includes Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining and Computer-Aided Design (CAD), have further more advantageous the precision and efficiency of crankshaft production. These technologies enable producers to model and check components clearly earlier than production, reducing mistakes and improving average satisfactory.
Technological Advancements
Recent developments in crankshaft era have targeted on enhancing engine performance and overall performance:
- Weight Reduction: Engineers were operating to lessen the burden of crankshafts with out compromising strength. Lighter crankshafts make a contribution to improved engine responsiveness and gas efficiency. Techniques which includes optimizing the shape and geometry of the crankshaft, in addition to the usage of advanced materials, were employed to achieve weight reduction.
- Enhanced Durability: The use of superior substances and surface remedies has caused crankshafts which could withstand better loads and showcase greater resistance to wear and fatigue. This outcomes in longer engine lifestyles and reduced protection requirements.
- Precision Engineering: The integration of CNC machining and CAD technologies permits for the manufacturing of crankshafts with extremely good precision. This precision results in better engine balance, reduced vibrations, and progressed usual overall performance.
Applications in Modern Engines
The function of the crankshaft extends beyond conventional inner combustion engines. In hybrid and electric vehicles, crankshafts are critical to variety extenders and other auxiliary energy units. Innovations in crankshaft design are also contributing to the improvement of greater green and effective engines in motorsports and high-performance vehicles.
Maintenance and Common Issues
Proper maintenance of the crankshaft is vital for engine toughness. Regular oil changes and the usage of remarkable lubricants help prevent put on at the crankshaft bearings. Common problems encompass bearing wear, cracks, and imbalance, which can result in engine vibrations and, if left unaddressed, intense engine harm. Early detection through habitual inspections can prevent high priced upkeep.
Conclusion
The crankshaft stays a pivotal factor in engine design, with ongoing advancements improving its performance and efficiency. As car era continues to conform, the crankshaft’s position adapts, making sure it meets the needs of cutting-edge engines. Understanding its function, layout, and the latest technological tendencies provides insight into the complexities of engine mechanics and the continuous pursuit of car excellence.

